Taipei, Taiwan – Greater than another nation, China holds the ability to make or break world efforts to stop a local weather disaster.
The world’s second-largest financial system is the biggest polluter globally, producing 27 % of emissions and greater than the USA, European Union, India, Russia and Japan mixed, in response to a 2021 evaluation by the Rhodium Group.
On the similar time, Beijing is eking out a spot as a pacesetter in renewable power, build up extra solar energy capability than your entire remainder of the world.
However whereas developed economies are lowering their emissions – albeit too slowly to fulfill their Paris Settlement pledges – China’s emissions are hovering resulting from a livid urge for food for coal used to energy its cities and energy-intensive industries like metal.
China’s emissions grew by 10 % year-on-year through the second quarter of this 12 months – placing it on the right track to beat its earlier document of 11.47-11.9 billion metric tonnes in 2021, in response to knowledge compiled by Carbon Transient, a United Kingdom-based web site centered on local weather coverage.
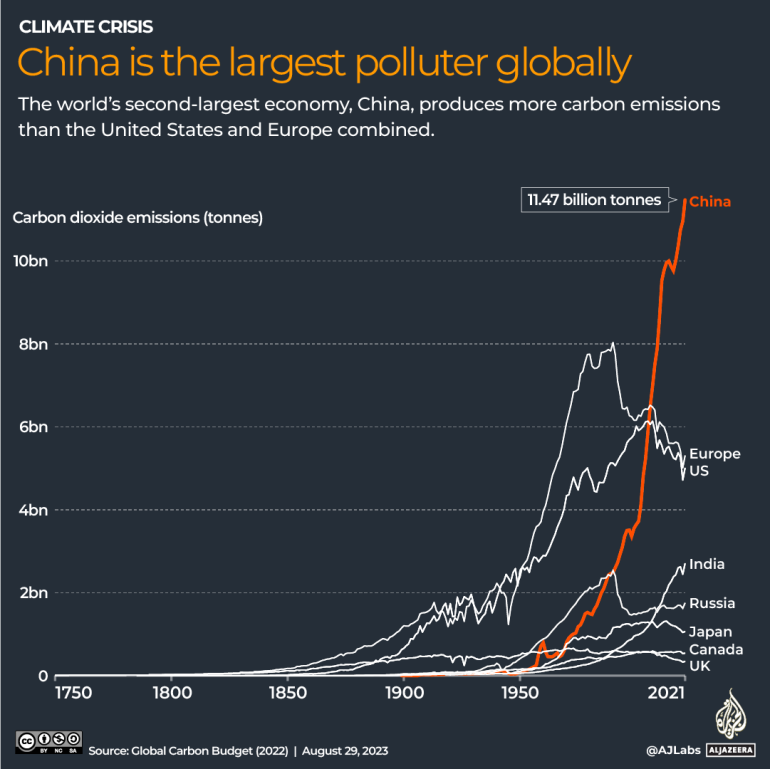
Left unchecked, the rising carbon footprint threatens to derail worldwide efforts to handle the local weather disaster, which scientists say already fall far quick of what’s wanted to mitigate the worst outcomes of rising temperatures.
The Chinese language financial system’s heavy reliance on coal is extensively anticipated to persist for years to come back, whereas local weather specialists worry that Beijing’s purpose of “peak carbon” by 2030, even when achieved, should be unacceptably excessive.
In the meantime, China’s renewable power targets, although bold, face appreciable obstacles, together with an outdated energy grid and the continuing problem of storing renewable power, analysts say.
“Nobody frankly comes near China’s management in renewables, second place is sort of distant,” Cory Combs, affiliate director of Trivium China, a coverage analysis firm, informed Al Jazeera.
“Then again, China is outpacing the remainder of the world on coal as properly.”
In 2020, Chinese language President Xi Jinping pledged to cut back his nation’s emissions by 65 % from their 2005 degree by 2030 and attain carbon neutrality by 2060.
Whereas Xi reiterated these targets in July, the Chinese language chief included a caveat: power coverage could be based mostly on the nation’s wants and never “swayed by others”.

Pushed by issues about its future power safety, Beijing has lately launched into a constructing spree of coal-fired energy crops.
Chinese language authorities authorised 86 gigawatts (GW) of recent coal-fired crops in 2022 alone, and green-lit 50GW extra within the first six months of 2023, in response to Greenpeace.
In complete, China presently has 243 GW of recent coal-fired energy services within the pipeline, sufficient to energy Germany, in response to a report by the Centre for Analysis on Power and Clear Air (CREA) and World Power Monitor.
“The most important story proper now might be the power safety perspective. China is not going to quit coal till it has a assure of efficient power safety,” Combs mentioned.
“Particularly, we’re taking a look at: one, the flexibility to offer base-load energy at any given time; and two, the flexibility to ensure that it will possibly meet any specific peak load.”
Beijing’s resolution to double down on coal displays fears of a repeat of power crunches which have troubled the trade lately.
In 2021, coal shortages and surging demand for items from factories through the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in blackouts in 20 Chinese language cities and provinces. The next summer time, a drought sparked by a record-breaking heatwave diminished the capability of the nation’s hydropower dams, which make up 16 % of China’s energy combine.

Confronted with back-to-back crises, provinces reminiscent of Guangdong started to extend their coal energy capability to make sure they’d not face the identical points sooner or later, mentioned David Fishman, a senior challenge supervisor on the Lantau Group, an financial consultancy specialising in Asia-Pacific’s energy and fuel markets.
“We may draw a fairly clear line there [that] any individual within the financial planning power workplace in Guangdong was wanting on the similar mock-up we did and went, ‘We’re susceptible to a severe drought in Yunnan, we have to add extra backup capability’,” Fishman informed Al Jazeera.
China’s document emissions of current years might, actually, underplay the nation’s trajectory as carbon-heavy industries like development and metal skilled severe disruption resulting from lockdowns in huge cities and manufacturing centres.
Nonetheless, some local weather specialists consider that peak carbon in China continues to be achievable by 2030 – though the scale of the height may range significantly relying on political elements.
Boyang Jin, a senior carbon analyst on the UK-based LSEG, mentioned the brand new coal-fired energy crops are meant as a stopgap measure solely and provincial governments will nonetheless be anticipated to fulfill local weather targets set by the highly effective Nationwide Improvement and Reform Fee.
“With increasingly more renewable capability put into operation, coal-fired crops will inevitably lower their output, or working hours,” Jin informed Al Jazeera.
“These crops will probably be step by step reworked from base load to peak load. Subsequently, it’s not at odds with carbon neutrality pledges.”
Nonetheless, political dangers loom.
China’s slowing financial system may encourage Beijing to try to construct its option to financial development because it has completed previously, whereas the highly effective metal trade might resist efforts to rein in emissions, analysts say.
“The height is in sight, it’s achievable, the preconditions are there however there’s a threat for these two causes that the height will get delayed till very late within the decade and that would single-handedly derail the worldwide local weather effort,” Lauri Myllyvirta, a lead analyst and co-founder of the Centre for Analysis on Power and Clear Air, informed Al Jazeera.

China’s investments in renewables have proceeded at an unprecedented tempo.
Beijing topped the checklist of traders in clear power in 2022 with $546bn – half of the worldwide complete that 12 months, in response to BloombergNEF knowledge.
China’s present wind and photo voltaic capability is sufficient to meet about 30 % of the nation’s power wants, in response to authorities knowledge.
Translating that funding into dependable power, nevertheless, is just not a easy process in follow.
Within the case of many wind and photo voltaic farms, there’s a vital hole between how a lot energy may be generated on paper and the way a lot may be really used.
Greenpeace has estimated that China’s precise power generated from renewables will solely improve by lower than 1 % per 12 months into the 2030s.
A lot of the hole is because of China’s restricted capability to retailer and transport energy generated from renewable sources to areas of excessive demand.
Whereas 94 % of China’s inhabitants lives to the east of the “Heihe-Tengchong Line” – an imaginary line dividing the nation from northeast to southwest – many hydropower dams and solar energy and wind farms are positioned in sparsely-populated areas within the west.
Different challenges embrace authorities intervention within the power market to maintain electrical energy costs artificially low, encouraging extreme consumption.

Fishman mentioned China’s bid for carbon neutrality will rely upon its profitable adoption of burgeoning applied sciences reminiscent of carbon seize and inexperienced hydrogen over the subsequent few many years.
“The actual query is 2060, however clearly it’s far off,” he mentioned. “It depends on loads of applied sciences which can be removed from being mature and scalable and cost-effective.”
Till then, China’s reliance on coal appears set to remain, analysts say.
“Coal is just not obligatory in precept, however there must be much more funding and there must be loads of market reform to be able to make that sensible,” Trivium China’s Combs mentioned.
“And till they’re actually in place, it’s coal. And so we get left in the established order, the place you have got large investments in renewables and continued funding in coal.”
